What is Zener diode
A Zener Diode, also referred to as a breakdown diode, is a specially doped semiconductor device engineered to function in the reverse direction. When the voltage across a Zener diode’s terminals is reversed and reaches the Zener Voltage (also known as the knee voltage), the junction experiences a breakdown, allowing current to flow in the opposite direction. This phenomenon, known as the Zener Effect, is a key characteristic of Zener diodes.

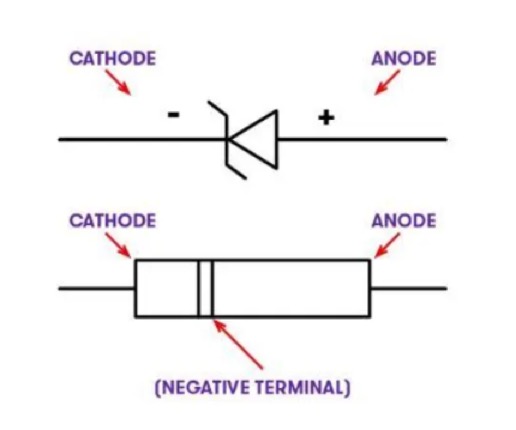
Circuit Symbol of Zener Diode
Zener diodes come in various packaging options, depending on their power dissipation requirements. Some are designed for high-power applications, while others are available in surface mount formats. The most commonly used Zener diode is packaged in a small glass enclosure, with a distinctive band indicating the cathode side of the diode.
How Zener diodes work
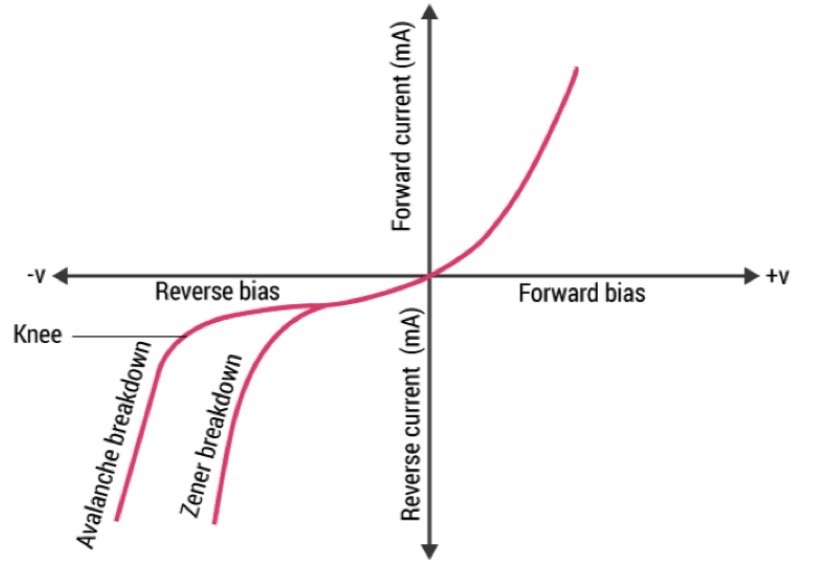
The working principle of a Zener diode depends on the reason for its breakdown under reverse bias conditions. There are usually two types of breakdown – Zener breakdown and Avalanche breakdown.
Zener breakdown
Zener breakdown occurs under a reverse bias voltage of 2V to 8V. The strength of the electric field is sufficient to exert force on the valence electrons, separating them from the atomic nucleus – even at such low voltages. This process forms movable electron hole pairs, thereby increasing the flow of current.
Zener breakdown typically occurs in diodes with high doping, high electric field strength, and low breakdown voltage. As the temperature increases, valence electrons gain more energy, thus requiring a lower applied voltage. This also means that the Zener breakdown voltage decreases with decreasing temperature.
Avalanche breakdown
For lightly doped diodes with high breakdown voltage, voltage breakdown can also occur under reverse bias conditions (with a breakdown voltage of at least 8V). The electrons flowing through the diode collide with the electrons in the covalent bond, thereby breaking the covalent bond. As the voltage increases, the speed of electrons also increases, which means that covalent bonds are more easily broken. It is worth noting that the avalanche breakdown voltage increases with temperature
Characteristics of Zener Diode
Characteristics of Zener diode
Forward Characteristics
Reverse Characteristics
Forward Characteristics of Zener Diode
The first quadrant in the graph represents the forward characteristics of a Zener diode. From the graph, we understand that it is almost identical to the forward characteristics of P-N junction diode.
Reverse Characteristics of Zener Diode
When a reverse voltage is applied to a Zener voltage, a small reverse saturation current Io flows across the diode. This current is due to thermally generated minority carriers. As the reverse voltage increases, at a certain value of reverse voltage, the reverse current increases drastically and sharply. This is an indication that the breakdown has occurred. We call this voltage breakdown voltage or Zener voltage, and Vz denotes it.
Topdiode produces PIN to PIN alternative to replace zener diode from Vishay, Nexperia, Onsemi, etc.
Cost down 30~60%,
Better lead time
Engineer team to do “cross to”
Support sample in free & trial order
There will be experienced engineers do cross reference and choose the match series for you.
| BZX55C (Topdiode zener diode BZX55C) |
| BZV55C(Topdiode Zener diode BZV55C Mini melf) |
| MM3Z2V0-MM3Z75-Topdiode |
| ZM4728~ZM4761-Zener Diodes -Topdiode |
| 1N4678-1N4717-Topdiode |
| 1N5333B-1N5388B-Topdiode |
| MM1Z5231C-MM1Z5262C-Topdiode |
| MM3Z2B4-MM3ZB75-Topdiode |
| MM1Z5221B~MM1Z5267B-BL SILICON PLANAR ZENER DIODES |
| MM1Z4689~MM1Z4717 SILICON PLANAR ZENER DIODES |
| MM1Z2V0~MM1Z75-BL Silicon Planar Zener Diodes |
| 1N4727A…1N4761A Silicon Planar Power Zener Diodes |
| BZX84C- Topdiode |
| MM3Z2V2B~MM3Z39B-Topdiode |