The total capacitive charge (Qc) of Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Barrier Diode (SBD) is small, reducing switching loss while enabling high-speed switching operation. In addition, unlike Si-based fast-recovery diodes where the trr (reverse recovery time) increases along with temperature, silicon carbide (SiC) devices maintain constant characteristics, resulting in better performance.
Like other SiC devices, SiC SBDs allow manufacturers to reduce the size of industrial equipment and consumer electronics, making them ideal for use inpower-factor correction circuits and inverters.
Topdiode offers SiC Schottky Barrier Diodes for rectification applications in assorted styles, including TO220-2, TO247-3, TO252, and DFN8x8, as they make power-conversion systems more reliable, they are routinely found in battery chargers, charging circuits for electric and hybrid vehicles, and in solar panels, they well suited for high frequency Switched-Mode Power Supplies.

Structure and Working
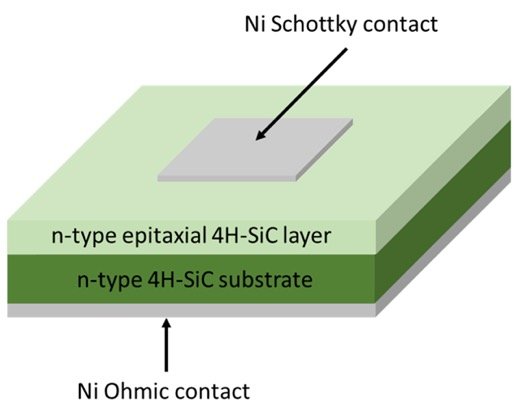
The structure of a Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Barrier Diode (SBD) consists of a metal contact, often made of platinum (Pt) or titanium (Ti), on a thin layer of n-type SiC semiconductor material. The metal contact forms the Schottky barrier with the SiC material, creating a rectifying contact that allows for the flow of current in only one direction. The thickness of the SiC layer is typically in the range of a few micrometers, and the doping concentration is carefully controlled to optimize the performance of the device. The SiC material is often grown on a substrate of silicon (Si) or sapphire, which provides mechanical support and thermal management. The resulting device has a high electric field strength, low leakage current, and fast switching speed, making it suitable for high-power and high-frequency applications.
The working principle of a Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky diode is based on the metal-semiconductor junction known as the Schottky barrier. When a metal (typically aluminum or platinum) is deposited on a SiC substrate, a Schottky barrier is formed between the metal and the semiconductor material. Unlike traditional P-N junction diodes, the Schottky diode does not have a depletion region, which leads to a lower forward voltage drop and faster switching speed.
In forward bias, the metal contact is connected to the positive terminal of a voltage source, while the SiC substrate is connected to the negative terminal. When a positive voltage is applied, the electrons from the metal contact are injected into the SiC substrate, resulting in a flow of current through the device. The forward voltage drop in a SiC Schottky diode is typically lower than in a traditional P-N junction diode, which leads to lower power losses and higher efficiency.
In reverse bias, the metal contact is connected to the negative terminal of a voltage source, while the SiC substrate is connected to the positive terminal. When a negative voltage is applied, the Schottky barrier width increases, and the electric field across the device increases, leading to a breakdown of the device at a certain voltage, known as the reverse breakdown voltage. The reverse breakdown voltage of SiC Schottky diodes is typically higher than in traditional P-N junction diodes, which makes them suitable for high-voltage applications.
SiC Schottky Barrier Diodes Advantage
| * Wide Bandgap, Low Loss
Improves efficiency in high-power applications |
| * High-Switching Speeds
Increases power density and reduces system size |
| * High Temperature (175°C) Operation
Improves reliability in harsh environments |
| * Soft-Switching Behavior Reduces EMI
Reduces passive component count |
| * Forward Voltage Positive Temperature Coefficient
Simplifies operational stability, allows paralleling |
| * High Surge Current Capability
Increases robustness and reliability |
Applications of SiC Schottky Barrier Diodes
Schottky Barrier Diode is a type of power diode that offers low forward voltage drop and has a fast switching speed. Schottky diodes can be used in applications where two parallel power supplies generate current. They also prevent reverse current flow from one supply entering the other. Schottky barrier diode is ideal for use in applications such as SMPS, power factor correction, solar inverter, DC/DC converters, industrial motor loads, wind generation inverter, UPS, clipping & clamping circuits, communication receivers, auxiliary power supply, freewheeling function, and reverse battery polarity protection.
Future Advancements on SiC Schottky Barrier Diodes
The future of SiC Schottky Barrier Diodes (SBDs) looks promising, as ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving their performance and reducing their costs. One area of development is the optimization of the SiC material and device design, which can lead to higher performance, better reliability, and lower cost. Another area of development is the integration of SiC SBDs with other power devices such as SiC MOSFETs, which can lead to improved overall system performance and efficiency. The integration of SiC SBDs with other power devices can also reduce the overall system cost, as the number of components and complexity of the system can be reduced.
Additionally, ongoing research is focused on improving the manufacturability and scalability of SiC SBDs, which can lead to a reduction in their cost and wider adoption. As the demand for high-performance power devices continues to grow in various applications such as electric vehicles, renewable energy, and aerospace, the development and adoption of SiC SBDs are expected to increase.
Furthermore, SiC SBDs are expected to play a significant role in the development of next-generation power electronics, including the integration of SiC SBDs with other wide bandgap devices such as GaN and SiC power transistors. The combination of these devices can lead to further improvements in performance and efficiency.
In conclusion, the future of SiC SBDs looks promising as research and development efforts continue to improve their performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. The continued adoption and integration of SiC SBDs in various applications are expected to contribute to the growth of the power electronics industry and the transition toward a more sustainable future.
Topdiode offer the following Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode, which cross for Infineon, Cree, on-semi. For further question or inquiries, please kindly contact Loie: sales4@topdiode.com, or visit our website: www.topdiodes.com thanks
650V 5A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode TPDG5S65C1P
650V 10A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-220-2 Package TPDA10S65C1
P650V 10A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-252 Package TPDG10S65C1P
650V 15A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-220-2 Package TPDA15S65C1P
650V 15A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-263 Package TPDG15S65C1P
650V 20A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Barrier Diode with TO-220-2 Package TPDB20A65C1P
650V 20A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-247-3 Package TPDD20A65C1P
650V 20A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-263 Package TPDG20A65C1P
650V 30A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode TPDD30A65C1P
650V 40A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode TPDH40S65C1P
1200V 10A Silicon Carbide (SiC) schottky Diode TPDH10S120C1P
1200V 20A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-247-2 Package TPDH20S120C1P
1200V 20A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-247-3 Package TPDD20A120C1P
1200V 40A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-247-2 Package TPDH40S120C1P
1200V 40A Silicon Carbide (SiC) Schottky Diode with TO-247-3 Package TPDD40A120C1P
1500V 10A Silicon Carbide (SiC) schottky Diode TPDH10S150C1P
1700V 10A Silicon Carbide (Sic) Schottky Diode TPDH10S170C1P



