In modern electronics, N Channel MOSFET (n-type metal oxide semiconductor) and P Channel MOSFET (p-type metal oxide semiconductor) are the basic units that constitute complementary metal oxide semiconductor circuits. These two types of metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) have significant differences in structure, performance and application, and their complementary relationship is also the cornerstone of building efficient electronic circuits.
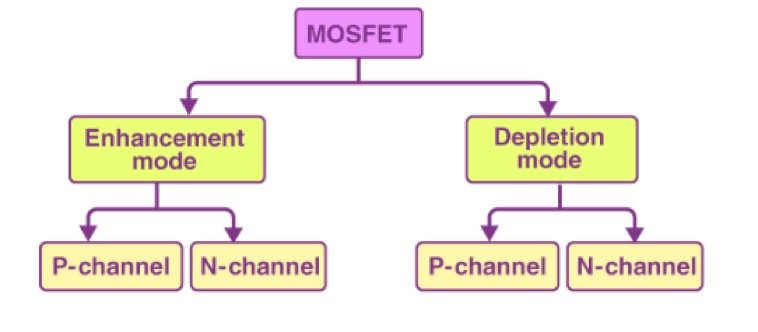
Basic differences between NMOS and PMOS
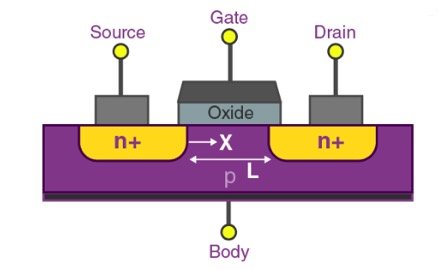
Material and structure
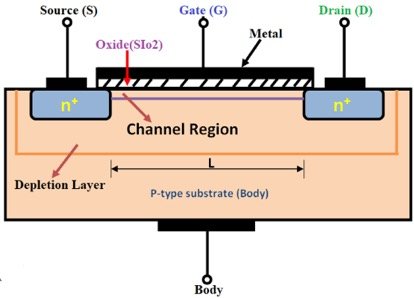
N Channel MOSFET: In n-type MOSFET, the source and drain are doped with n-type materials, and the gate controls the passage of electrons as the main carriers. Current is formed when electrons flow from the source to the drain.
P Channel MOSFET: In p-type MOSFET, the source and drain are doped with p-type materials, and the gate controls the passage of holes as the main carriers. Current is formed when holes flow from the source to the drain.
Operating voltage
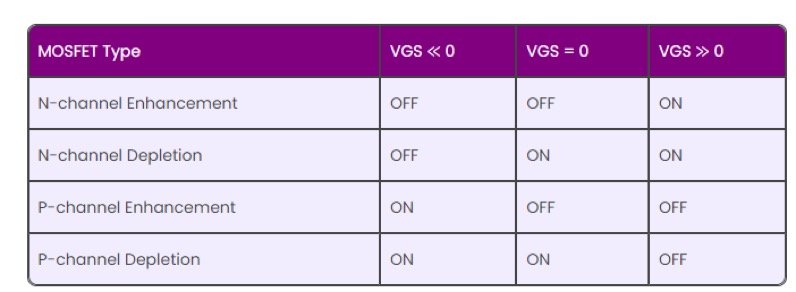
N Channel MOSFET: requires a positive gate-source voltage (V_GS) to turn on the channel and allow current to pass. That is, a positive voltage is applied between the gate and the source.
P Channel MOSFET: requires a negative gate-source voltage to turn on the channel and allow current to pass. That is, a negative voltage is applied between the gate and the source.
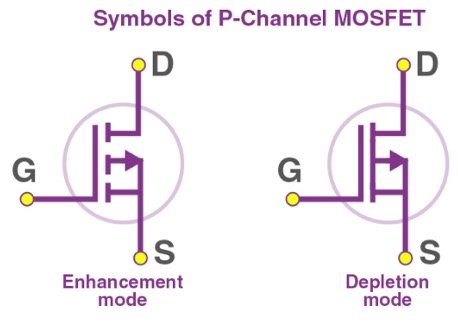
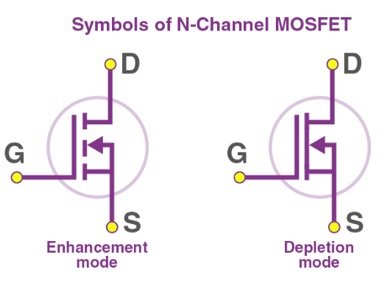
Symbols
N Channel MOSFET: In the circuit diagram, there is an arrow between the source and drain pointing toward the gate, indicating the direction of electron flow.
P Channel MOSFET: In the circuit diagram, there is an arrow between the source and drain pointing away from the gate, indicating the direction of hole flow.
Performance comparison between NMOS and PMOS
Carrier mobility
N Channel MOSFET: Electrons have higher mobility and can move faster in semiconductor materials. Therefore, NMOS devices are usually faster than PMOS devices.
P Channel MOSFET: The mobility of holes is lower, resulting in slower speed of PMOS devices.
On-resistance:
N Channel MOSFET: Due to high-mobility electrons, NMOS devices have lower on-resistance and can conduct large currents with smaller voltage drops.
P Channel MOSFET: The mobility of holes is lower, so the on-resistance of PMOS devices is higher.
Power consumption:
N Channel MOSFET: In logic circuits, due to high power consumption, such as in CMOS structures, usually only one transistor is turned on, so the power consumption is lower.
P Channel MOSFET: When PMOS is used alone, the power consumption is higher, especially in low-power circuits or low-voltage applications.
Relationship between N Channel MOSFET and P Channel MOSFET
The important complementary relationship between N Channel MOSFET and P Channel MOSFET is reflected in CMOS technology. The following are the advantages of CMOS technology:
Low power consumption: CMOS circuits consume almost no power when static and only consume power when switching states, which greatly reduces the overall power consumption and is an ideal choice for low-energy electronic devices.
High noise tolerance: CMOS circuits have a wide voltage swing, which can provide a higher noise tolerance and improve the reliability and stability of the circuit.
High-speed performance: Although P Channel MOSFET is slower, in CMOS technology, due to the high-speed characteristics of N Channel MOSFET devices, the overall circuit can achieve high-speed operation.
Dense integration: CMOS technology allows high-density integrated circuit design, making electronic devices more and more miniaturized and more and more powerful.
Summary
N Channel MOSFET and P Channel MOSFET are important basic components in the semiconductor field. They have their own advantages and disadvantages, but they complement each other perfectly in CMOS technology. N Channel MOSFET has the advantages of fast speed and low on-resistance, while PMOS has better anti-interference ability. The combination of the two not only excels in low power consumption and high-speed performance, but also greatly promotes the miniaturization and high-efficiency development of integrated circuits.
The complementary relationship between N Channel MOSFET and P Channel MOSFET occupies an important position in integrated circuit design. Understanding and rationally utilizing these characteristics will help design more efficient and reliable electronic systems.
TOPDIDOE’s MOSFET Part Numbers:
MOSFET SOT-23 P-Channel BSS84
MOSFET SOT-23 P-Channel TP3401D
MOSFET SOT-23 N-Channel BSS123
MOSFET SOT-23 N-Channel BSS138
MOSFET SOT-23 N-Channel TAP2302B
MOSFET SOT-23 N-Channel 2N7002
MOSFET SOT-23 P-Channel TAP2305
MOSFET SOT-23-3 P-Channel Power TP3407
MOSFET SOT-23-3 N-Channel Enhancement TP3400A
MOSFET SOT-23-3 P-Channel Power TP3003
MOSFET SOP-8 P-Channel Enhancement TP4409S
MOSFET SOP-8 N+P-Channel Power TP4616
MOSFET PDFN3*3-8L N-Channel TP30H80Q
MOSFET PDFN3*3-8L N-Channel TP85N4Q
MOSFET PDFN3*3 N-Channel TP4008QD
MOSFET PDFN5*6-8L N-Channel TP80N06G
MOSFET TO252 N-Channel TP50N06K
If you want to explore more MOSFTS, please visit our website: www.topdiodes.com
Or send inquiry to karin@topdiode.com