A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). Transistors can be used in rectifiers as switches to control the flow of current.
How rectifiers and transistors work together
A transistor rectifier circuit can be made with a transistor, a biasing diode, and some resistors.
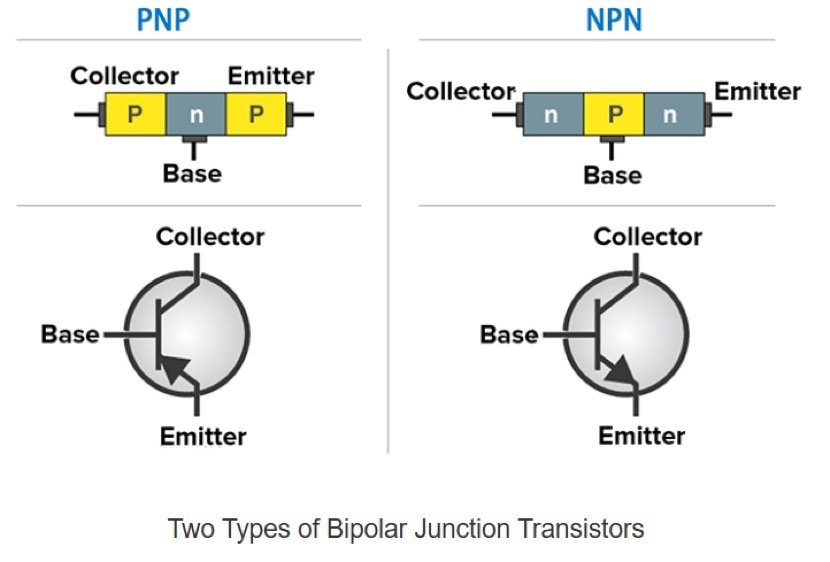
The type of transistor used determines whether the rectification is for the positive or negative half cycle.
The transistor acts as a switch that controls the flow of current.
Rectifier types
Half-wave rectifier: A simple rectifier that eliminates one side of the AC, making it inefficient
Full-wave rectifier: A more efficient rectifier that uses both sides of the AC waveform
Transistor series rectifier: An electronic circuit that uses a transistor to convert AC to DC
Rectifier applications
Rectifiers are often used in DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems.
They are also used in power supplies for radio, television, and computer equipment.
Rectifier performance
The quality of the rectification process is measured by the ripple factor, which indicates the fluctuations in the rectified DC output.
Transistor (bipolar) is just 2 back to back diodes. Take NPN (below) as an example, you have basically a collector-base diode in series with an emitter-base diode. For a transistor with a very wide base width (large distance from collector to emitter), it behaves just like two diodes. If you bias a very wide base width “transistor” in the active region, all your emitter current becomes base current due to all minority carriers (electrons) end up recombined in the base region; and none of the electron would make it to the collector, which is what 2 diodes would do.
However, when the base width is made smaller and smaller, wonderful thing happens. When the base width is small enough (much smaller than diffusion length of electrons in the base region), almost no recombination would take place in the base region; most of the minority carriers (electrons) get across the base region through diffusion and swept across the collector-base depletion region by the electric field. These electrons becomes the collector current. This is the transistor action that we know.
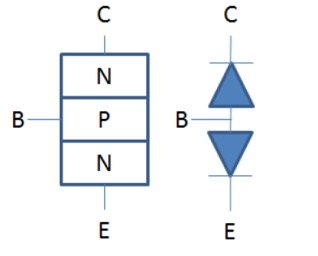
Transistors are composed mainly of silicon, a semiconductor material. They have three layers and two pn junctions: an emitter (which emits carriers), a base (which controls the carrier movement), and a collector (which collects carriers). The region between these layers is very thin compared to the other two.
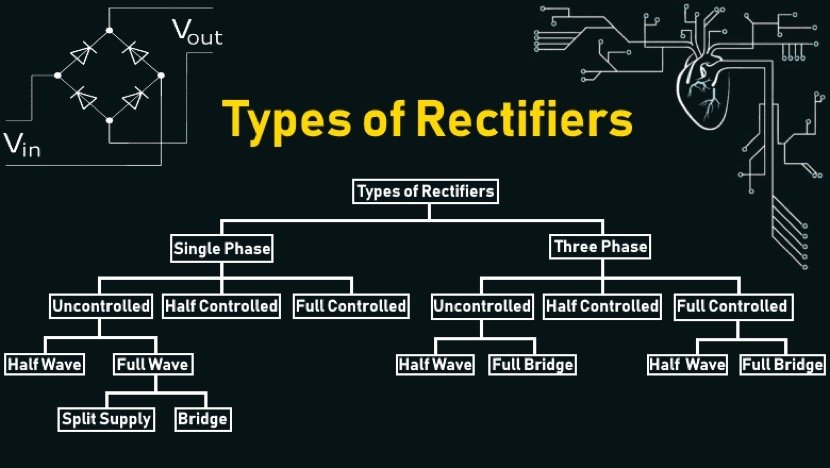
In electronics, Rectifier circuit is the most used circuit because almost every electronic appliance operates on DC (Direct Current) but the availability of the DC Sources are limited such as electrical outlets in our homes provide AC (Alternating current). The rectifier is the perfect candidate for this job in industries & Home to convert AC into DC. Even our cell phone chargers use rectifiers to convert the AC from our home outlets to DC. Different types of Rectifiers are used for specific applications.In electronics, Rectifier circuit is the most used circuit because almost every electronic appliance operates on DC (Direct Current) but the availability of the DC Sources are limited such as electrical outlets in our homes provide AC (Alternating current). The rectifier is the perfect candidate for this job in industries & Home to convert AC into DC. Even our cell phone chargers use rectifiers to convert the AC from our home outlets to DC. Different types of Rectifiers are used for specific applications.
Usually, the types of Rectifiers are classified based on their output. In this article, we will discuss many types of Rectifiers such as:
Single Phase Rectifiers
Three Phase Rectifiers
Controlled Rectifiers
Uncontrolled Rectifiers
Half Wave Rectifiers
Full Wave Rectifiers
Bridge Rectifiers
Center-Tapped Rectifiers
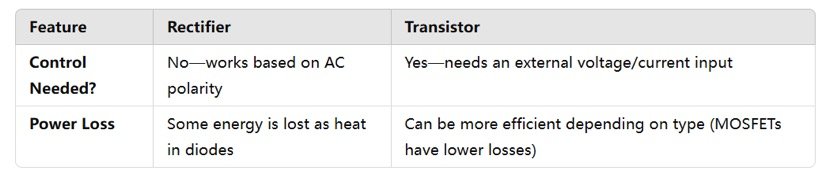
Rectifiers and transistors are both semiconductor devices, but they serve different functions in electronic circuits.
Function & Purpose
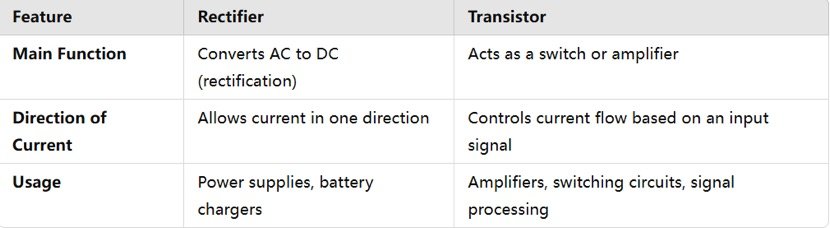
Working Principle
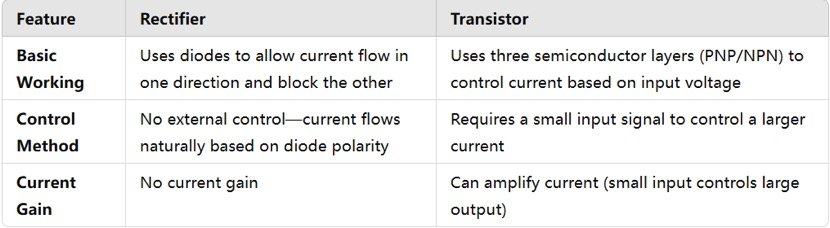
Types & Structure
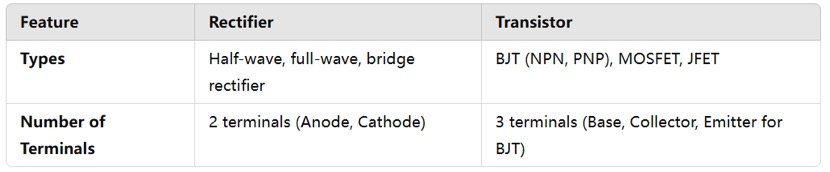
Applications
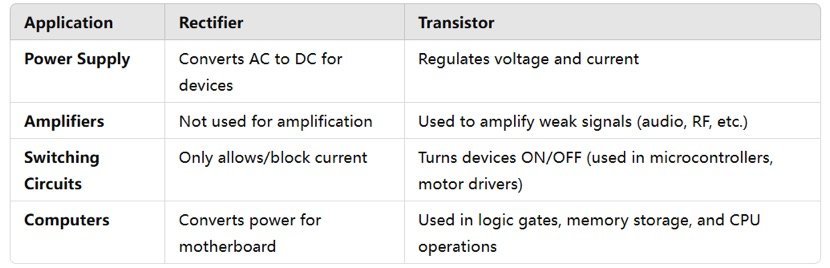
Control & Efficiency
If you need DC power from AC, you use a rectifier.
If you need switching or amplification, you use a transistor.
For further question or inquiries, please kindly contact Loie: sales4@topdiode.com, or visit our website: www.topdiodes.com thanks



