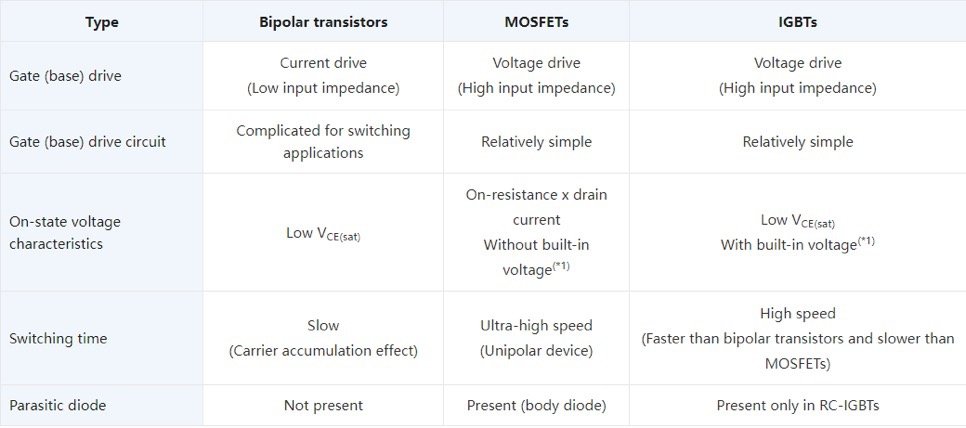
There are three major types of transistors: bipolar transistors, MOSFETs, and IGBTs. The following table compares the performance and characteristics of these transistors. Bipolar transistors are now hardly ever used for power electronics and switching applications because of the need for drive and protection circuits and slow switching speed.
Comparison of the performance of different types of transistors
Switching Loss: IGBTs generally have higher switching losses compared to MOSFETs due to their internal structure and the need for a gate driver.
Switching Speed: MOSFETs generally have faster switching speeds compared to IGBTs, which can be advantageous in applications that require rapid switching or precise control.
Voltage Ratings: IGBTs typically have higher voltage ratings compared to MOSFETs, which makes them more suitable for high-voltage applications.
The main difference between IGBT and MOSFET is the switching loss(more switching loss in IGBT), Switching speed(MOSFETs are faster) and voltage ratings(IGBTs have higher voltage ratings).
IGBTs

Advantages:
High current handling capability
Low on-state voltage drop
Good thermal performance
Robust construction
Disadvantages:
High switching losses
Slow switching speed
MOSFETs

Advantages:
Low switching losses
Fast switching speed
Small size
Disadvantages:
Lower current handling capability
Higher on-state voltage drop
Poor thermal performance
Difference Between IGBT and MOSFET
IGBTs: IGBTs are typically used in applications where high current handling capability and low on-state voltage drop are essential, such as heavy Duty inverters/UPSs. They are also used in applications requiring high thermal performance, such as electric vehicles and industrial drives.
MOSFETs: MOSFETs are typically used in applications with low switching losses and fast switching speeds, such as switching power supplies and motor control, which are essential. They are also used in applications where small size is essential, such as Inverter/UPS having 100VA to 4 KVA to be safer.

IGBT and MOSFET FAQs
Q1: Why we prefer IGBT
Answer: The IGBT has advantages over the power MOSFET and BJT. It has a very low ‘ON’-state voltage drop and better current density in the ‘ON’ state. This allows for a smaller die size with the possibility of more economical manufacturing costs. Driving IGBTs is simple and requires low power.
Q2: What is the advantage of IGBT?
Answer: IGBTs offer several advantages such as high voltage/current handling, fast switching speed, and low saturation voltage
Q3: What is the main purpose of IGBT?
Answer: IGBTs are widely used as switching devices in the inverter circuit (for DC-to-AC conversion) for driving small to large motors. IGBTs for inverter applications are used in home appliances such as air conditioners and refrigerators, industrial motors, and automotive main motor controllers to improve their efficiency
Q4: What is the main advantage of IGBT over SCR?
Answer: The main advantage of IGBT over SCR is its self-commutating capability i.e. it has a capability of being turned-on or turned-off at will by use of some form of low power (either voltage or current controlled) signal into a third (gate or base) terminal.
Q5: Why IGBT is used for high voltage?
Answer: Compared to MOSFETs, IGBTs also are better suited to scale in current handling capability at higher voltage levels due to their bipolar output characteristics.
For further question or inquiries, please kindly contact Loie: sales4@topdiode.com, or visit our website: www.topdiodes.com thanks



