MPSA42U NPN Silicon Epitaxial Planar Transistor Topdiode
- Epitaxial Planar Die Construction
- Complementary PNP Type Available
- Ideally Suited for Automated Assembly Processes
- Ideal for Medium Power Switching or Amplification Applications
- RoHS compliant
Topdiode MPSA42U NPN Silicon Epitaxial Planar Transistor
Topdiode MPSA42U is NPN Silicon Epitaxial Planar Transistor for high voltage switching and amplifier
applications.
Topdiode MPSA42U is NPN Silicon Epitaxial Planar Transistor with SOT-89 plastic Package.
Topdiode MPSA42U is a nice alternative offer for Diodes DXTA42
Topdiode MPSA42U NPN Silicon Epitaxial Planar Transistor DATA
- Tab
| Topdiode PN | MPSA42U |
| Description | NPN Silicon Epitaxial Planar Transistor |
| Package | SOT-89 |
| Polarity | NPN |
| Ptot (mW) | 250 |
| VCEO [max] (V) | 65 |
| IC [max] (mA) | 100 |
| hFE [min] | 110 |
| hFE [max] | 450 |
| Tj [max] (°C) | 150 |
| Cross to Brand | Diodes |
| Pin to Pin Cross P/N | DXTA42 |
Topdiode Hot Selling Products (6)
Transistor Datasheet
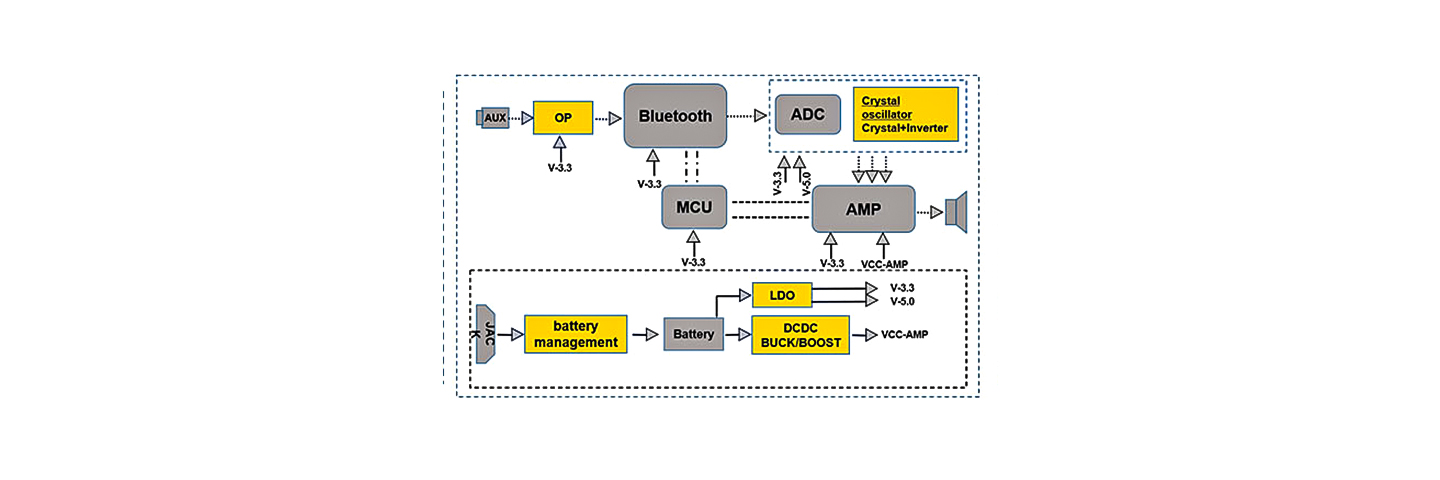
Topdiode Transistors Used on Bluetooth Audio Speaker
Topdiode transistors MMBT8050 MMBT8550 MMBT3904 and mosfets TP3400 TP3401 TP3407 are used on Bluetooth Audio Speaker
The development of speakers has shifted from traditional TV speakers to portable Bluetooth speakers and WiFi speakers. In the past two years, with the rise of the IoT, it has driven the further development of smart Bluetooth audio speakers.

Topdiode Transistor Applications



A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and power. Typically, transistors consist of three layers, or terminals, of a semiconductor material, each of which can carry a current.
When working as an amplifier, a transistor transforms a small input current into a bigger output current. As a switch, it can be in one of two distinct states — on or off — to control the flow of electronic signals through an electrical circuit or electronic device.
The most basic and important characteristic of the transistor: the transistor has a current amplification effect. Its essence is that the transistor can control a large change in the collector current with a small change in the base current.
It has three major applications:
1. Used in amplifier circuits for voltage or current amplification;
2. Used in oscillation circuits for modulation, demodulation or self-oscillation;
3. Used in switching circuits as thyristors, current limiting or switching tubes.
1. Provide signal amplification to ensure a fair output for the application.
2. Regulate an incoming signal’s current and voltage.
3. Smaller and lighter than vacuum tubes, while also being mechanically stronger.
4. Require no external heating for operation.
5. A low-voltage supply is sufficient to operate a transistor.
6. Highly suitable for low-power applications.
7. Ideal for integrating with resistors and diodes to create integrated circuits.
8. As the size of transistors decreased exponentially, their cost has fallen.