What is a Transistor?
A transistor is a device that regulates voltage flow, or current. In simple terms, a transistor acts as a gatekeeper or switch for handling electronic signals. Three primary semiconductor components, able to carry an electric current, comprise a transistor. These materials are often silicon or germanium.
The transistor was developed in 1947 by Bell Labs. Initially, it was an alternative to vacuum tubes for regulating electronic signals.
What is a transistor in simple words: A gatekeeper for handling electronic signals.

How Transistors Work
A transistor is essentially a switch that can control the flow of electric current. It has three terminals: the emitter, the base, and the collector in a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), or the source, the gate, and the drain in a Field-Effect Transistor (FET). The behavior of the transistor depends on the voltages applied to these terminals.
In a BJT, a small current applied to the base-emitter junction allows a much larger current to flow from the emitter to the collector. This current amplification is a key feature of BJTs. The ratio of the output current (collector current) to the input current (base current) is called the current gain, denoted by the symbol β.
In a FET, the flow of charge carriers between the source and drain terminals is controlled by an electric field, which is created by applying a voltage to the gate terminal. Unlike BJTs, FETs do not require a base current to operate, which makes them more energy-efficient.
The ability of transistors to control the flow of electric current makes them useful in a wide range of applications. They can be used to amplify signals, as in audio amplifiers and radio transmitters, or to switch signals on and off, as in digital circuits. By combining millions or even billions of transistors on a single chip, it is possible to create complex electronic devices like microprocessors and memory chips.
Types of Transistors
Transistors come in a variety of types, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The two most common types are the Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) and the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET).
The BJT is a transistor that uses both electron and hole charge carriers, and it comes in two types: NPN and PNP. It consists of three layers of semiconductor material, called the emitter, base and collector, forming two pn junctions. BJTs are known for their high current gain and are commonly used in audio amplifiers and signal-processing circuits.
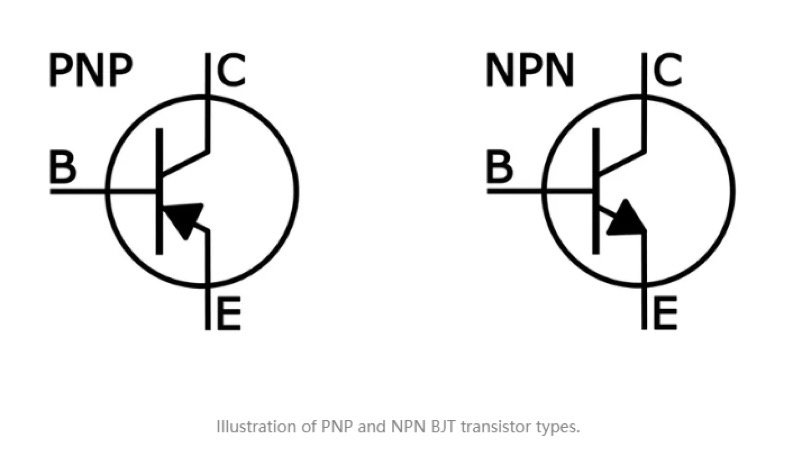
The MOSFET, on the other hand, is a type of field-effect transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of charge carriers, and it comes in two types: n-channel and p-channel, depending on whether they use electrons or holes as charge carriers. It has four terminals: the source, gate, drain, and body, whereas the gate voltage determines whether the MOSFET conducts or insulates. MOSFETs are widely used in digital circuits and microprocessors due to their high input impedance and low power consumption.
In addition to these two types, the Junction Field-Effect Transistor (JFET) is another transistor that uses a pn junction to control the flow of charge carriers rather than a metal-oxide layer. JFETs have a high input impedance and are commonly used in input stages of amplifiers and oscillators.
The Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is yet another type of transistor that combines the high input impedance of a MOSFET with the high current-carrying capability of a BJT. IGBTs are commonly used in power electronics, such as inverters and electric motor drives.
Finally, the FinFET is a type of MOSFET that uses a 3D structure to improve control of the current flow, enabling further miniaturization and improved performance. FinFETs are used in the latest generation of microprocessors and memory chips.
In conclusion, each type of transistor has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which to use depends on the specific requirements of the application. Regardless, all transistors operate based on the same basic principles of semiconductor physics and charge carrier behavior.
Topdiode produces high-quality Transistor for crossover, we have replacements for Nexperia, Diodes, SEMTECH & On-semi, please check below:
| Topdiode PN | Package | Cross to Brand | Pin to Pin Cross to P/N |
| BC8456DE~BC8458DB | SOT-563 | Nexperia | BC847BVN |
| MPSA42U | SOT-89 | Diodes | DXTA42 |
| MMBT2222A | SOT-23 | Diodes | MMBT2222A |
| MMBT2907 | SOT-23 | On-Semi | MMBT2907 |
| MMBT3904 | SOT-23 | Diodes | MMBT3904 |
| MMBT7002 | SOT-23 | SEMTECH | MMBT7002 |
| MMBT8050 | SOT-23 | SEMTECH | MMBT8050 |
| BC817-BC818 | SOT-23 | Nexperia | BC817 series |
If you want to explore more component,
please visit our website:https://www.topdiodes.com
Or send inquiry to : Luna@topdiode.com



